The global wind power market continues to rapidly expand in 2015. It is expected that global wind energy production will surpass 65 gigawatts by 2020!
Wind Energy Timeline – From Persian Windmills Crushing Grains to Vesta's Wind Turbines Churning out 8 MW of Output
Pradhnya Tajne | Transparency Market Research
.jpg)
The global wind energy industry has gone through many ups and downs in the past few centuries. However, the 20th and 21st century proved to be the most crucial for the wind energy sector. Several significant innovative technologies were shaped during these two centuries.
The use of wind energy can be dated back to the Egyptian civilization, where it was used in sailboats. Currently, there exist wind turbines with capacities to generate an output of around 8 megawatts! Let us look at the most significant events in the history of wind energy.
3,500 BC till 900 AD
-
3,500 BC: Egyptians invented the first sailboats. These boats were propelled using wind.
-
2,000 BC: According to historical data, windmills were used to pump water in China
-
500 to 900 AD: Persians innovated windmills that were used to crush grains and pump water

1100s
Wind power began appearing in several regions of Europe during the medieval period. Windmills in Europe were used to crush grain
1300s
The Dutch built windmills that were used to drain water from low-lying regions. These windmills were the first to have a horizontal-axis structure. The technological enhancements of these windmills allowed superior grain grinding and water pumping.
1600s
The Dutch introduced their innovative windmill designs to the New World
1700s
Windmills lost some of their importance during the 1700s due to the Industrial Revolution
1800s
-
Early 1800s: Windmills started to appear in the Great American Plains as the settlers moved towards the West. The settlers started using windmills to pump water along the western frontier.
-
1850s: The U.S. Wind Engine Company was established by John Burnham and Daniel Halladay. They build the Halladay Windmill which was designed for the West American landscape.
-
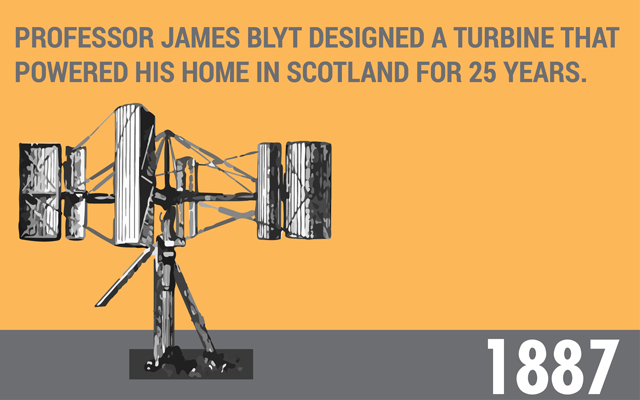
1887:
In July 1887, the first windmill for electricity generation was built by Professor James Blyth in Glasgow, Scotland. Out of the three different turbine designs, the last design is said to have powered the Professor’s home for 25 years.
Towards the end of year, Professor Charles Brush developed a 12kW capacity wind turbine to charge 408 batteries stored in his mansion. The turbine was functional for 20 years and boasted a rotor diameter of 50m and 144 rotor blades.
-
1890s: Six million windmills were reportedly installed across America. Windmills started using steel blades which boosted efficiency. The Chicago World’s Fair presented 15 windmill companies and their turbine designs.

1900s
-
1920s
Wind turbines began to provide electricity to thousands of rural regions across the Great Plains
French inventor, Georges Jean Marie Darrieus developed a turbine called the ‘eggbeater’, which stood out for its slender vertical axis turbine
In 1927, Marcellus and Joe Jacobs establish the Jacobs Wind company. The firm produced wind turbine generators that were used on farms to power lighting and charge batteries.
-
1931: Russia constructed the first commercial power plant that employed wind turbines to produce electricity
-
1941: In Vermont, the world’s first megawatt-size wind turbine started operations to combat fuel shortage
-
1950s: A majority of wind turbines in the U.S. are shut down due to disuse due to the advent of affordable fossil-fuelled stationary engines and widespread of rural electrification
-
1970s
In 1971, the first offshore wind farm in the world began operations off the coast of Denmark
The drastic spike in oil prices causes great interest in the renewable energy sector in 1973
In 1977, the United States Department of Energy (DOE) is formed. The National Renewable Energy Laboratory begins operations.
-
1980s
The government in the U.S. delivers tax credits for the use of renewable power
The first wind farm in the world is constructed at New Hampshire in the U.S. However, due to turbine break down and overestimation of wind as a resource, the project is deemed a failure.
1985: A wind farm in California powers around 250,000 homes. However, wind turbine capacities are still inadequate at this time.
1989: Federal funding for wind energy research experienced a decline through the decade, and DOE funding reached a low point in 1989
-
1990s
Increasing public concerns about environment issues such as global warming raise interest in renewable energy again
In 1991, the U.K.’s first onshore wind farm is opened in Cornwall. The farm had a capacity of 10 turbines that supplied enough power for 2,700 homes.
In 1992, the Energy Policy Act in the U.S. announces a production tax credit of 1.5 cents per kWh of wind energy generated electricity. It aims its focus on increasing use of renewable energy.

2000s
-
2000: The price of electricity generated using wind power was between 4 to 6 cents per kWh
-
2001: Wind energy capacity reached a total of 24,800 megawatts. The global wind power market generated approximately US$7 billion revenue.
-
2003: Legal compliance in Europe encouraged the growth of wind energy in this region. Europe boasted a massive 70% of total global wind energy production.
-
2004: The price of electricity generated using wind power falls to 3 to 4 cents per kWh
-
2005: The updated Energy Policy Act in the U.S. supports incentives for renewable energy sources. The total global wind energy production continues to demonstrate an exponential growth.
-
2006: Global wind power production exceeded 74,000 megawatts
-
2007: The U.S. wind power capacity climbed by an impressive 45%
-
2008: The European Union established a target for the U.K. government in order to increase their contribution of renewables to 20% till 2020 to drastically decrease greenhouse gas emissions. The global wind energy installed capacity crossed 94,000 megawatts.
-
2009: Wind energy provided 2% of the total global electricity usage
-
2010: Cape Wind received approval by the Federal Government as the first offshore wind farm in America
-
2012: Wind energy powered 15 million homes in the U.S. and became the primary source of renewable electricity
-
2013: The first offshore wind farm in Canada is planned for coastal British Columbia. 110 turbines are expected to contribute to generate 396 megawatts of power.
-
2014: Wind energy alone contributes 20-30% of the annual electricity demand in nations such as Denmark and Spain
The global wind power market continues to rapidly expand in 2015. It is expected that global wind energy production will surpass 65 gigawatts by 2020!

Kramer commented, “My dream is that one day you’ll have two technicians with Ghostbusters backpacks come to your house and spray your roof”.
The content & opinions in this article are the author’s and do not necessarily represent the views of AltEnergyMag
Comments (0)
This post does not have any comments. Be the first to leave a comment below.
Featured Product

